The emergence of multiple blockchain networks like Ethereum, Solana, and Polkadot has led to an increasingly multi-chain world. However, a major challenge is that these different blockchains cannot easily communicate with each other out-of-the-box. This severely limits what decentralized applications (dApps) can achieve, since they can only leverage the capabilities of one chain at a time.
That’s where blockchain interoperability protocols like the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) come in.
Developed by the blockchain middleware company Chainlink, CCIP provides a standardized way for smart contracts on different blockchains to seamlessly communicate.
This enables a whole new world of cross-chain dApps that can harness the unique strengths of multiple networks. With CCIP, tokens, data, and commands can be sent across chains, unlocking revolutionary new use cases.
In this beginner’s guide, we’ll explore what CCIP is, how it works under the hood, real-world applications being built on it, and why interoperability protocols like CCIP are so important for the future of Web3.
Quick Verdict: Chainlink’s Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) enables seamless communication between smart contracts across different blockchains, unlocking a new generation of cross-chain decentralized applications.
What is CCIP?
CCIP stands for Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol. In simple terms, it is a standard that enables smart contracts on different blockchains to communicate with each other.
Before CCIP, if you had a decentralized application on Ethereum that wanted to interact with another app on a blockchain like Solana, it was extremely difficult. That’s because the underlying infrastructure of each chain is unique. They have their own isolated set of accounts, contracts, tokens, and methods for sending transactions.
CCIP provides a common language that all these disparate blockchains can understand. It acts as a translation layer that allows sending and receiving of messages across networks. This messaging system allows transferring data, tokens, or both across chains.
Cross-chain by Chainlink
CCIP was developed by the blockchain company Chainlink. They already provide a decentralized oracle network that allows smart contracts to access off-chain data. Expanding their infrastructure to support generalized communication between chains was a natural evolution.
The vision is for CCIP to become an open standard that any blockchain can adopt. By integrating CCIP, chains and applications gain interoperability with the whole ecosystem. This opens up a new world of possible cross-chain use cases.
Key Capabilities
Arbitrary Messaging – This allows sending raw data encoded as bytes to a smart contract on another chain. Developers can encode any instructions they want to trigger actions on the receiving chain. For example, they could encode orders to mint NFTs or execute complex workflows.
Token Transfers – CCIP supports transferring tokens directly to smart contracts or EOAs (externally owned accounts controlled by users) on other chains. This allows assets to seamlessly move across blockchain environments.
Programmable Token Transfers – This advanced capability combines token transfers with arbitrary messaging. Users can send tokens along with custom instructions on what to do with them in a single cross-chain transaction. For instance, a user could send tokens as collateral to take out a flash loan on another chain.
The key is that CCIP provides a generalized messaging framework, not just token bridging between specific chains. Developers build customized cross-chain applications using the flexible building blocks CCIP offers.
Receiving accounts can be smart contracts or EOAs:
Smart contracts can receive arbitrary data and tokens.
EOAs can receive tokens but not data messages.
This architecture allows CCIP to support advanced cross-chain dApps as well as simple token transfers.
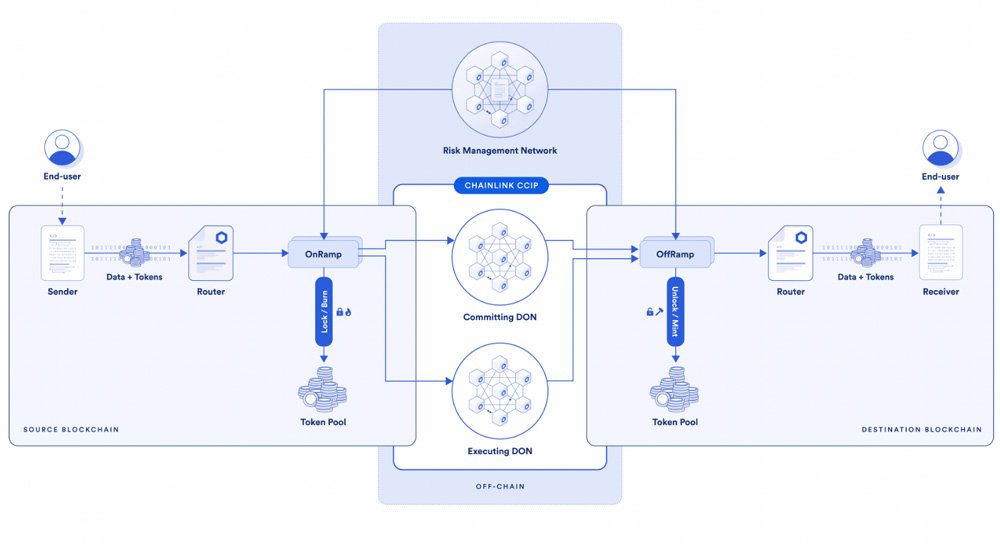
Architecture
Under the hood, CCIP utilizes a layered architecture that allows it to achieve security, reliability, and interoperability between heterogenous blockchains.
At the base layer, CCIP relies on Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network. This is made up of independent node operators that provide reliable off-chain computation and data delivery to blockchains.
CCIP uses an upgraded version of Chainlink’s Off-Chain Reporting protocol (OCR). This enables secure and efficient consensus among oracle nodes off-chain, which is crucial for cross-chain communication.
On top of the oracle layer, CCIP introduces a novel Risk Management Network. This is comprised of independent oracle nodes monitoring the health of CCIP’s services. If any issues are detected, it can trigger automated shutdown to prevent losses.
At the core is the CCIP messaging protocol itself. This defines common standards and APIs for sending and receiving data across chains. Smart contracts integrate these APIs to seamlessly harness cross-chain communication.
On top of CCIP, additional modules can be built, like token bridges or data relays between specific chain pairs. Users can also build customized UI interfaces to access CCIP’s cross-chain capabilities.
This modular architecture maximizes flexibility and interoperability across all blockchains. Developers can mix and match components to build bespoke cross-chain applications.
Use Cases
CCIP unlocks a myriad of new cross-chain use cases that were previously very difficult or impossible to implement. Here are some examples:
Cross-Chain Lending – CCIP can facilitate lending and borrowing across decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols on different chains. Users get access to liquidity pools on multiple networks.
Yield Optimization – Users can leverage CCIP to move collateral across chains and maximize yields by taking advantage of protocol incentives and interest rates on multiple platforms.
Low-Cost Transactions – Chains with lower fees can be used for computation, while settlement occurs on more secure chains, reducing costs for users.
Data Availability – Data can be stored on chains with cheap storage like Polygon, while computation happens on chains like Solana, optimizing dApp designs.
Hybrid dApps – New types of dApps can be created that harness the unique strengths of different chains in a single application.
Metaverse/NFTs – CCIP can enable use cases like cross-metaverse asset portability and P2E gaming across chains.
Automated Workflows – Smart contracts can encode complex conditional workflows across chains using CCIP messaging.
The possibilities are endless when you start combining multiple isolated blockchains into a unified application! CCIP is the key infrastructure making these next-generation use cases a reality.
Adoption and Support
For an interoperability protocol like CCIP to succeed, it needs widespread integration across many chains, dApps, and infrastructure providers.
The good news is that Chainlink already has an extensive ecosystem. Over 100 unique chains and protocols actively use its oracle services. Many have expressed interest in adopting CCIP once released.
Leading chains like Ethereum, BNB Chain, Polygon, Avalanche, and Fantom are likely to be early integrators. These networks want to provide their dApp developers with easy cross-chain capabilities.
Many of the top DeFi protocols also plan to adopt CCIP. Initiatives like Aave Arc are already working on cross-chain versions of their platforms using CCIP for interoperability.
Finally, Chainlink’s own Programmable Token Bridge will provide a reference implementation showing how to use CCIP for secure token transfers.
Given Chainlink’s leading position in blockchain middleware, CCIP is poised to become a widely adopted standard for interoperability. This will create a truly interconnected ecosystem where dApps seamlessly harness the strengths of all networks.
Development Resources
Cross-Chain Website
Official Documentation
Conclusion
Chainlink’s Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) represents a major milestone in realizing the vision of a truly interconnected multi-chain future.
By providing a standardized messaging layer, CCIP enables seamless communication between smart contracts across isolated blockchains for the first time.
This unlocks revolutionary new cross-chain applications that can harness the unique capabilities of different networks in a single dApp. CCIP powers use cases like optimized yield farming, hybrid computations, interoperable NFTs, and much more.
Equally as important, CCIP offers a robust and secure infrastructure built on Chainlink’s time-tested oracle network. This provides reliability and protection for mission-critical cross-chain transactions.
As CCIP adoption grows across chains like Ethereum and Solana, it will usher in the next stage in the evolution of Web3 – where decentralized networks interoperate rather than compete.
The possibilities are endless when all blockchains can speak the same language. CCIP is the translation layer enabling this new multi-chain future.
The post What is Chainlink CCIP? Complete Beginner’s Guide appeared first on Blockonomi.