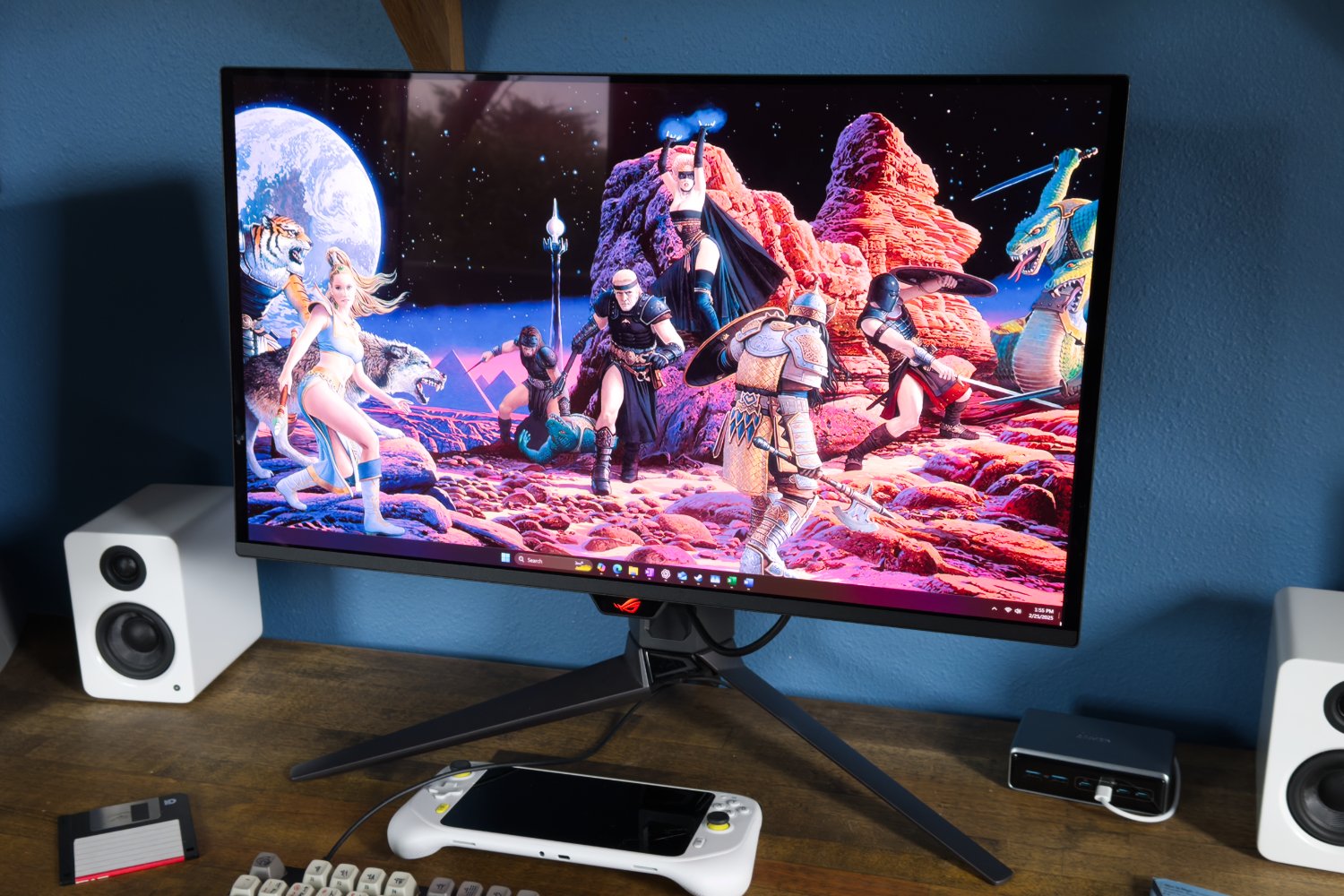
Screens with OLED panels are increasingly being used in laptops and PC monitors. The reason: The prices for OLEDs have fallen, and this is likely to continue in the future.
A laptop with an OLED display is currently available for as little as $750, such as the Lenovo Chromebook Plus 14.
You won’t find top equipment here, neither in terms of components nor the screen. However, the 60-hertz display offered in this device class masters most everyday tasks without any problems, as long as gaming is not involved.
A monitor with an OLED panel is often aimed at special application scenarios. It either supports creative work with outstanding detail or gaming on the computer with ultra-fast switching times.
An OLED gaming monitor with a 27-inch diagonal, QHD resolution and 240 hertz refresh rate is priced at a good $700 — such as the LG Ultragear OLED 27GS95QE-B. A 4K 32-incher such as the Dell 32 Plus (S3225QC) costs upwards of $800. This means that OLED monitors are still no bargain, but their prices are increasingly moving into affordable regions.

Matthew Smith / Foundry
Stumbling block: Burn-in due to static image content
Just like OLED televisions, OLED monitors also impress with their outstanding contrast. As they can dim with pixel precision and switch off the pixels completely, they display true black.
The self-illuminating pixels also impress with their rich colors, very short switching times, and extremely stable viewing angles, where colors hardly change at all, even when you look at the screen from the side.
What curbs the enthusiasm for OLED screens in the computer environment is the risk of burn-in. These effects can occur if image content is displayed statically for a long time.
In the case of televisions, this applies to channel and program logos, for example. There are far more possibilities when working on a desktop monitor or laptop display on a daily basis.
This is because many applications involve the display of static content — for example, tables, texts, or the Windows taskbar, which always remains visible in the default settings of the operating system.

Even if the OLED panel is not yet a bargain for PC monitors, many gaming screens, such as the LG Ultragear OLED 27GS95QE-B shown here, are now quite affordable.
LG
There are different levels of burn-in effects: image sticking, image retention, or ghost image is a temporary effect. A slight shadow image or outline remains visible even though the image signal has already changed.
The effect is caused by the fact that OLEDs react very sensitively to changes in the current voltage. If the threshold voltage of the pixel transistors shifts, the faulty picture can occur.
Proper burn-in or image retention, on the other hand, is permanent in OLEDs. Static content that is displayed repeatedly over a long period of time leaves permanent traces on the panel. You then see them as shadow images in the background that no longer disappear.
Burn-in occurs because OLED panels wear out during operation. They age and lose luminosity in the process. However, this is a very slow process. For this reason, genuine defects caused by burn-in are covered by most manufacturers’ device warranties.
In addition, the panel can compensate for a deficit in luminosity by increasing the power supply to precisely these pixels.
OLED maintenance support
For both desktop monitors and most laptops with OLEDs, the manufacturers offer built-in maintenance measures. You should definitely carry them out in order to maintain the panel quality.
In the case of monitors, you will find the integrated routines for OLED maintenance in the on-screen display (OSD). They are often located under the menu item “Other.”
Laptop manufacturers often integrate the functions into the manufacturer’s own maintenance tools. Asus, for example, has added the “Asus OLED Care” section to the MyAsus utility program for laptops with OLED panels.
In many cases, there are also additional apps for both device categories that support you with OLED care. However, the offer depends very much on the specific device.
Lenovo, for example, limits the Lenovo Display Refresh utility to the Thinkpad X1 Fold. At the same time, an update of the respective tool does no harm. In our experience, some OLED maintenance functions are only enhanced by an update.
Pixel refresh: Basic maintenance for the OLED screen
A common maintenance routine that is intended to prevent the risk of burn-in from the outset is the pixel refresh, or pixel update.
This measure checks and corrects the threshold voltage on the pixel transistors. This can shift in the course of OLED operation — especially when many bright areas are displayed.
This is where the most current flows and the highest temperature is generated as a result. The aim of the routine is to restore the threshold voltage that was set when the panel was produced. The correction also eliminates any display errors.
The pixel refresh starts automatically on most devices after a certain number of operating hours. Some monitor models, such as the Dell 32 Plus S3225QC, indicate in the OSD that a pixel refresh is necessary after just four hours.
Visually, a green dot at “OLED screen status” changes to yellow. In this case, however, we do not receive an active notification to intervene. If we start the correction, the process runs automatically and takes six to eight minutes. The display switches off at the end.
For good reason, the setting in the OSD cannot be deactivated. However, you can select that the refresh only starts when the monitor is in standby mode.
Taking a look at the OSD from time to time and performing the refresh will benefit the lifespan of your OLED monitor.
Panel refresh: Self-calibration of the OLED pixels
To prevent irreversible damage caused by real burn-in, all OLED panels have an integrated self-protection mechanism — panel refresh, also known as panel compensation.
The protection process starts automatically after a specified operating time. The device manufacturers are keeping quiet about when exactly this happens. However, several hundred operating hours have probably already passed.
The panel refresh starts as soon as the display is switched off. For this reason, you should not completely disconnect an OLED monitor from the power supply via a switchable power strip.
During panel refresh, the screen uses a memory function. The internal controller saves all the data on light duration and brightness — for each pixel.
Those OLED pixels that have been shining at high brightness for a particularly long time and have therefore already diminished in brightness are given a higher power supply.
This works because OLED panels do not usually light up in the maximum range, but on the basis of the Average Picture Level (APL). This describes in percent how high the average brightness of a picture on the screen is.
Further protective measures: Pixel shifting, logo dimming, and more.
Especially with OLED monitors and laptops intended for gaming, manufacturers integrate additional protective mechanisms for the OLED screen. However, not every model has to feature all of these processes.
Pixel shifting: This function is also known as pixel orbiter. If it is activated, the displayed image is shifted horizontally and vertically by a few pixels at predefined intervals — approximately every three minutes. This changes its position on the display. This is intended to prevent certain pixels from being overused and therefore ageing more quickly.
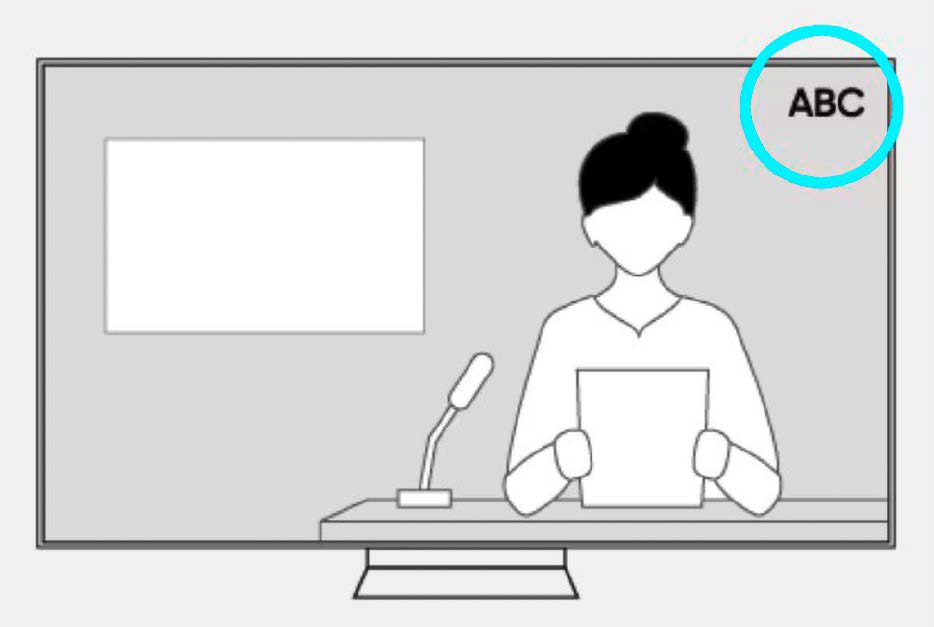

Logo recognition can be activated on some devices with OLED screens. It detects the static image content on the screen and darkens it to protect the panel from burn-in.
Foundry
Logo dimming/logo detection: If the operating menu of your monitor offers this function, the display automatically recognizes logos and recurring overlays and reduces their brightness. You can usually determine how much this should happen yourself using several levels. This setting is a precautionary measure that is useful for toolbars in games, channel logos, or program names.
Screen saver: To protect the entire display, you can activate a screen saver via the manufacturer’s tool. It starts as soon as there is no input signal — often after just two minutes.
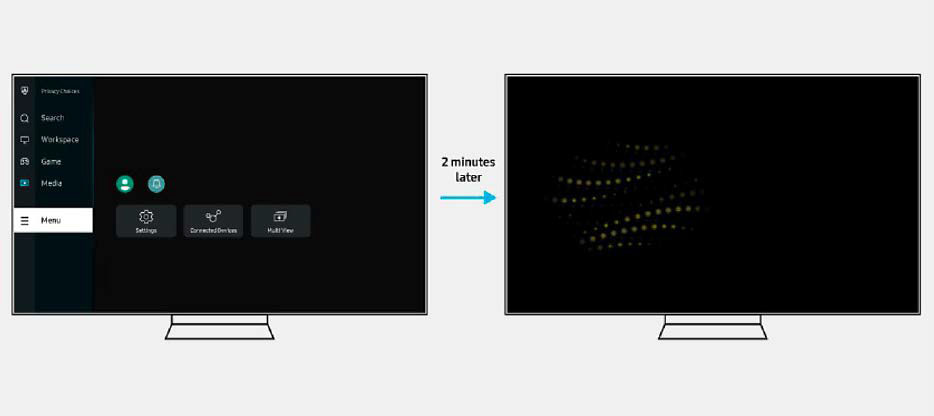
An activated screen saver — here on a Samsung OLED monitor — protects the display from damage caused by static content when the computer is not in use.
Foundry
OLED protection measures for everyone
With these measures, you can protect the valuable OLED screen from burn-in effects and preserve the lifespan of the pixels.
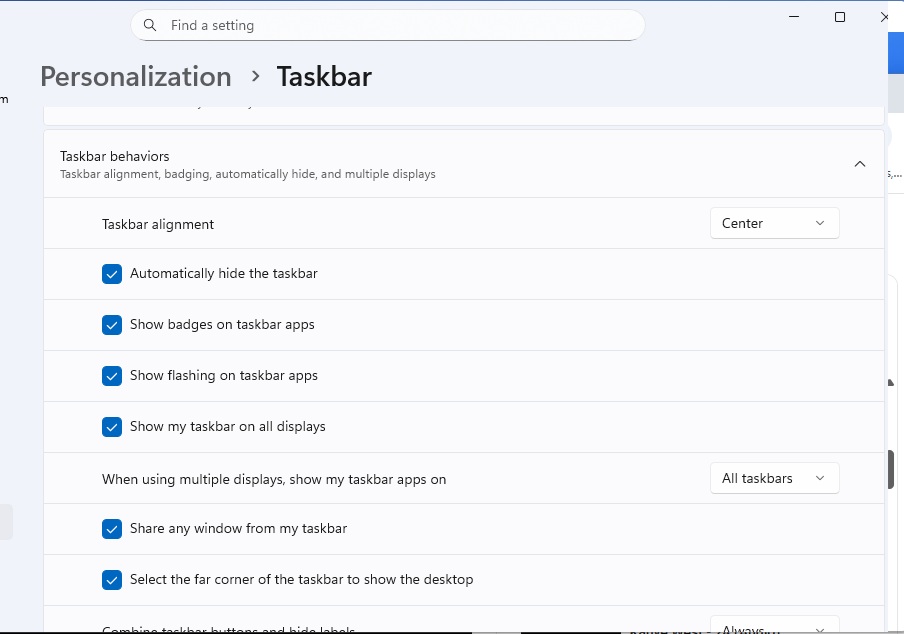
Hide the taskbar: On the computer, the Windows taskbar is one of those static contents that are always displayed. To protect the OLED pixels, you can prevent this by hiding the taskbar.
In Windows 11, right-click on the desktop and select “Personalize.” In the “Taskbar” area, scroll down to “Taskbar behaviors.” Tick the box next to “Automatically hide the taskbar.”
Screensaver: Even if your OLED device does not have a screensaver, you can activate it in Windows 11. Again, under “Personalize,” click on “Lock screen” and go to “Screen saver.”
Ideally, you should choose a dark color. You can display it in the preview and set a waiting time in minutes.
Foundry
Dark mode: Dark mode is a suitable means of further reducing the bright areas on the OLED screen. It is not only easy on the eyes, but also on the OLED panel. It can also be switched on in the Windows “Personalization” area. Click on “Colors” and select “Dark” under “Choose your mode.”
Full screen mode: Full screen mode is particularly recommended for watching films and videos, so that the video display is scaled to fit the entire screen area. Cinema fans should therefore pay attention to the 16:9 format at the time of purchase to avoid annoying bars on the sides.
Brightness control: With desktop monitors, ambient light sensors often regulate the brightness of the OLED screen depending on the conditions at the installation site. Depending on the situation, the luminance is automatically reduced.
For moving images such as films, it is advisable to use existing modes — such as film mode. If you use HDR settings, don’t forget to switch them off again. This reduces the peak brightness, protects the OLED pixels and also saves energy.
Related content
This articles is written by : Nermeen Nabil Khear Abdelmalak
All rights reserved to : USAGOLDMIES . www.usagoldmines.com
You can Enjoy surfing our website categories and read more content in many fields you may like .
Why USAGoldMines ?
USAGoldMines is a comprehensive website offering the latest in financial, crypto, and technical news. With specialized sections for each category, it provides readers with up-to-date market insights, investment trends, and technological advancements, making it a valuable resource for investors and enthusiasts in the fast-paced financial world.
