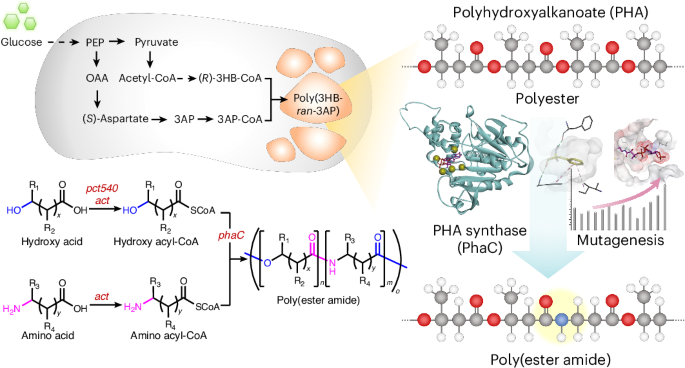
Polymers are one of the most important elements of modern-day society, particularly in the form of plastics. Unfortunately most common polymers are derived from fossil resources, which not only makes them a finite resource, but is also problematic from a pollution perspective. A potential alternative being researched is that of biopolymers, in particular those produced by microorganisms such as everyone’s favorite bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli).
These bacteria were the subject of a recent biopolymer study by [Tong Un Chae] et al., as published in Nature Chemical Biology (paywalled, break-down on Arstechnica).
By genetically engineering E. coli bacteria to use one of their survival energy storage pathways instead for synthesizing long chains of polyester amides (PEAs), the researchers were able to make the bacteria create long chains of mostly pure PEA. A complication here is that this modified pathway is not exactly picky about what amino acid monomers to stick onto the chain next, including metabolism products.
Although using genetically engineered bacteria for the synthesis of products on an industrial scale isn’t uncommon (see e.g. the synthesis of insulin), it would seem that biosynthesis of plastics using our prokaryotic friends isn’t quite ready yet to graduate from laboratory experiments.
This articles is written by : Nermeen Nabil Khear Abdelmalak
All rights reserved to : USAGOLDMIES . www.usagoldmines.com
You can Enjoy surfing our website categories and read more content in many fields you may like .
Why USAGoldMines ?
USAGoldMines is a comprehensive website offering the latest in financial, crypto, and technical news. With specialized sections for each category, it provides readers with up-to-date market insights, investment trends, and technological advancements, making it a valuable resource for investors and enthusiasts in the fast-paced financial world.